Description
Suture Material Suture Material
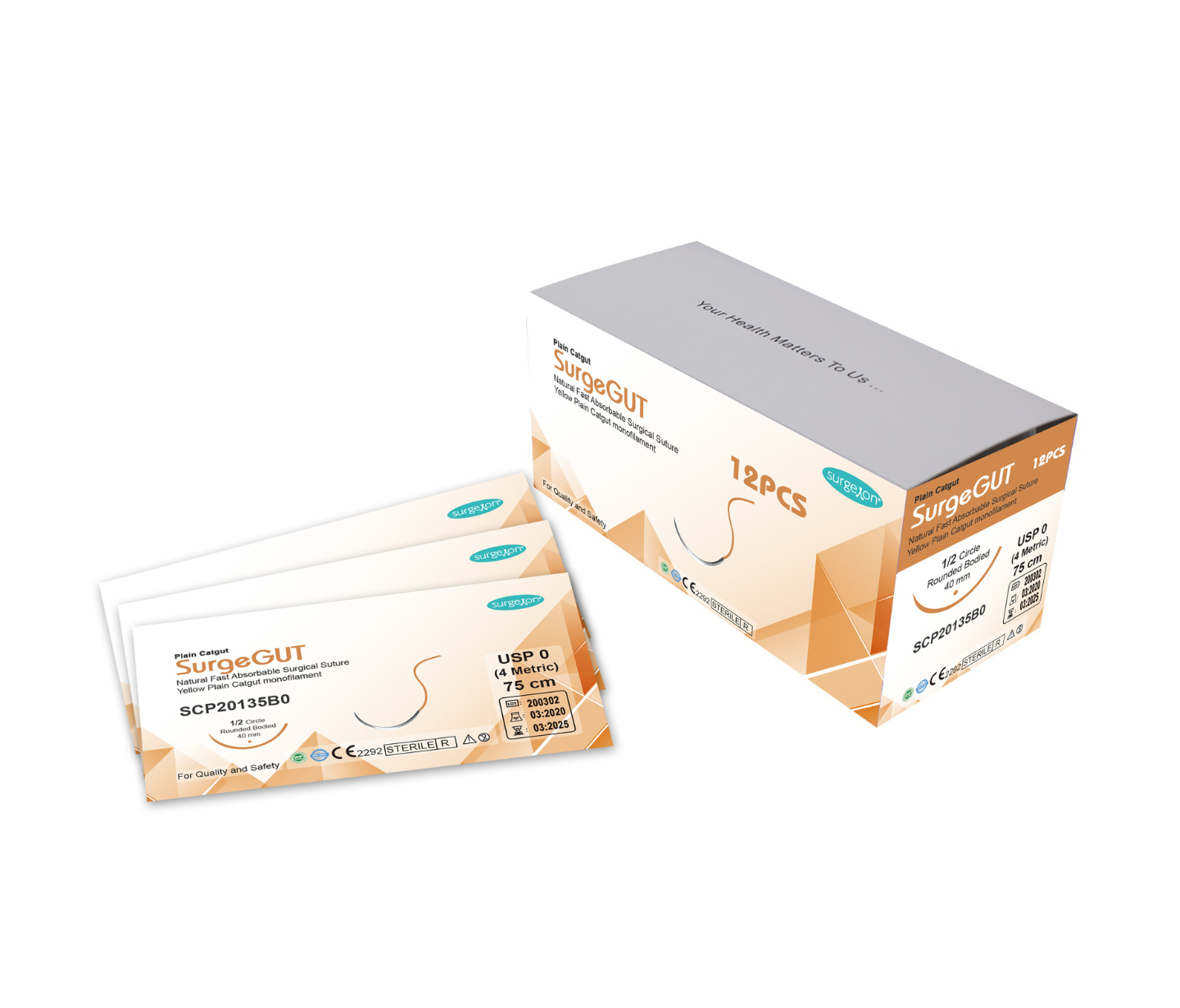
A surgical Catgut Plain suture is a sterile and absorbable surgical suture made from purified connective tissue, predominantly collagen, derived from the serosal layer of beef (bovine) intestines. There is also a variant called Chromic Gut, which contains a chromic salt solution to delay the absorption process. Both types of surgical gut sutures meet the requirements established by the United States Pharmacopeia (U.S.P.) for absorbable surgical sutures. They are indicated for use in general soft tissue approximation, and ligation, and are also suitable for ophthalmic procedures.
Actions Actions
When Surgical Gut Suture is introduced into the tissue, it triggers a moderate tissue inflammation, which is a typical foreign body response to the substance. Subsequently, the suture undergoes a gradual loss of tensile strength and suture mass as the proteolytic enzymatic digestive process dissolves the surgical gut. This process continues until the suture is completely absorbed. Several factors, such as the type of gut (Plain or Chromic), infection, and tissue sites, can influence the rate of absorption and tensile strength loss.
Characteristics Characteristics
Surgexon’s Plain Catgut suture is a sterile, absorbable surgical suture composed mainly of highly purified connective tissue (mostly collagen) sourced from either beef or sheep intestines. The suture is available in Beige color and exhibits an extremely short absorption period, leading to minimal tissue reaction. The quality of the suture often depends on its collagen percentage, which determines superior tensile strength, longer absorption times, and lower reactions in vivo. Surgexon manufactures its Plain Catgut sutures with the highest quality collagen, maintaining a composition of 97% - 98% pure collagen. The Plain Catgut is rapidly absorbed, and its tensile strength is maintained for approximately 10 days. Complete absorption takes place within 70 days, making it ideal for tissues that heal rapidly and require minimal support.
Indications Indications
It is crucial not to re-sterilize the suture, and any open or unused sutures should be discarded. Proper storage at cool room temperature is essential, avoiding prolonged exposure to elevated temperatures. Prolonged contact with salt solutions, such as those found in the urinary or biliary tracts, may lead to calculus formation. Users should be familiar with surgical procedures involving absorbable sutures to minimize the risk of wound dehiscence, which can vary based on the site of application and the suture material used. Acceptable surgical practices, including drainage and closure of contaminated or infected wounds, should be followed. The use of this suture may be inappropriate in patients with conditions that could delay wound healing. Surgeons should consider using supplemental non-absorbable sutures in sites undergoing expansion, stretching, or requiring additional support.
Precautions Precautions
In specific circumstances, such as orthopedic procedures, the surgeon may employ immobilization using external support. Skin sutures that need to remain in place for longer than seven (7) days may cause localized irritation and should be removed accordingly. Care should be taken during handling to avoid damage caused by surgical instruments like forceps or needle holders. Adequate knot security requires the accepted surgical techniques of flat, square ties, with additional throws as warranted by surgical circumstances and the surgeon's experience. Some patients may exhibit hypersensitivity to collagen or chromium, leading to immunological reactions with potential inflammation, tissue granulation, fibrosis, wound suppuration, bleeding, and sinus inflammation.
Adverse Reactions Adverse Reactions
Possible adverse effects associated with the use of this suture include wound dehiscence, inadequate wound support in the closure of certain areas such as the abdomen, chest, and joints where expansion, stretching, or distension occurs, insufficient support in elderly, malnourished, or debilitated patients, and in patients suffering from cancer, anemia, obesity, diabetes, infections, or other conditions that may delay wound healing. Other potential effects include enhanced bacterial infectivity, minimal acute inflammatory tissue reaction, localized irritation when skin sutures are left in place for more than seven (7) days, calculus formation in urinary and biliary tracts with prolonged contact with salt solutions like urine and bile, and pain, edema, and erythema at the wound site.
Brand Name Length Size
| Brand Name | Suture Material | Length | Size | |||||||||||
| SurgeGut | Plain Catgut |
|
|